Introduction
In this tutorial, we shall be configuring Bluetooth Devices to Communicate using Interrupts with each other using the knowledge gained from our previous tutorial How to setup and configure a ZS-040 HC-05 Bluetooth transceiver to create a mini application which will send messages back and forth between a master and a slave Bluetooth device. This will require two sets of hardware, not only for the Bluetooth devices themselves, but also 2 Identical Nucleo Boards, 2 ZS-040 (Master/Slave), and two FTDI devices for USART output on 2 different dumb terminal emulators.
The master device will be plugged into the “Master” Breadboard setup configured on USART2. The slave device will be plugged into the “Slave” Breadboard setup configured on USART3.
Current and Future Tutorials
- Part1 utilizes straight ASCII characters and deliniates the End-Of-Line (EOL) by finding the carriage return/line feed (CR/LF) bytes.
- Part2 will use the same hardware configuration, as Part 1. The main difference will be that instead of relying on the CR/LF bytes, the code is restructured to use a prefix of uint16_t to denote the size of the actual message.
- Part 3 again will use the same hardware configuration as Part 1 & 2. The difference in this tutorial will be that the prefix will be 4 ASCII bytes indicating the size of the actual message. We continue to use a software ring buffer, to alleviate the potential issue of a buffer overrun.
- Part 4 introduces a hardware DMA circular buffer, one that’s configured via the IOC file, to replace the software ring buffer. Part 4 will continue to use the same hardware configuration as Part 1-3.
Materials List
- FTDI to USB
- HS-040 Bluetooth Master/Slave Module
- Breadboards Kit Include 2PCS 830 Point 2PCS 400 Point Solderless Breadboards
- NUCLEO-F439ZI
FTDI Pinouts
FTDI to USB Pinout from right to left. The FTDI module is needed to convert the USART RX/TX signals into RS-232/USB such that you can interface with a dumb terminal.
- Pin 1 – GND
- Pin 2 – CTS
- Pin 3 – VCC
- Pin 4 – TX
- Pin 5 – RX
- Pin 6 – DTR
- USB Mini – Connect to PC via USB cable
Make sure the jumper is set for 5v or 3v which ever is being used to power the FTDI device. If we look below at the schematic, it is showing in this case as 5v. Also, validate that any hardware flow control is turned off.
If the dumb terminal emulator you are using has hardware flow control, you probably will not see the response to the <Enter> key being pressed and therefore the master Bluetooth device will not proceed to get configured.

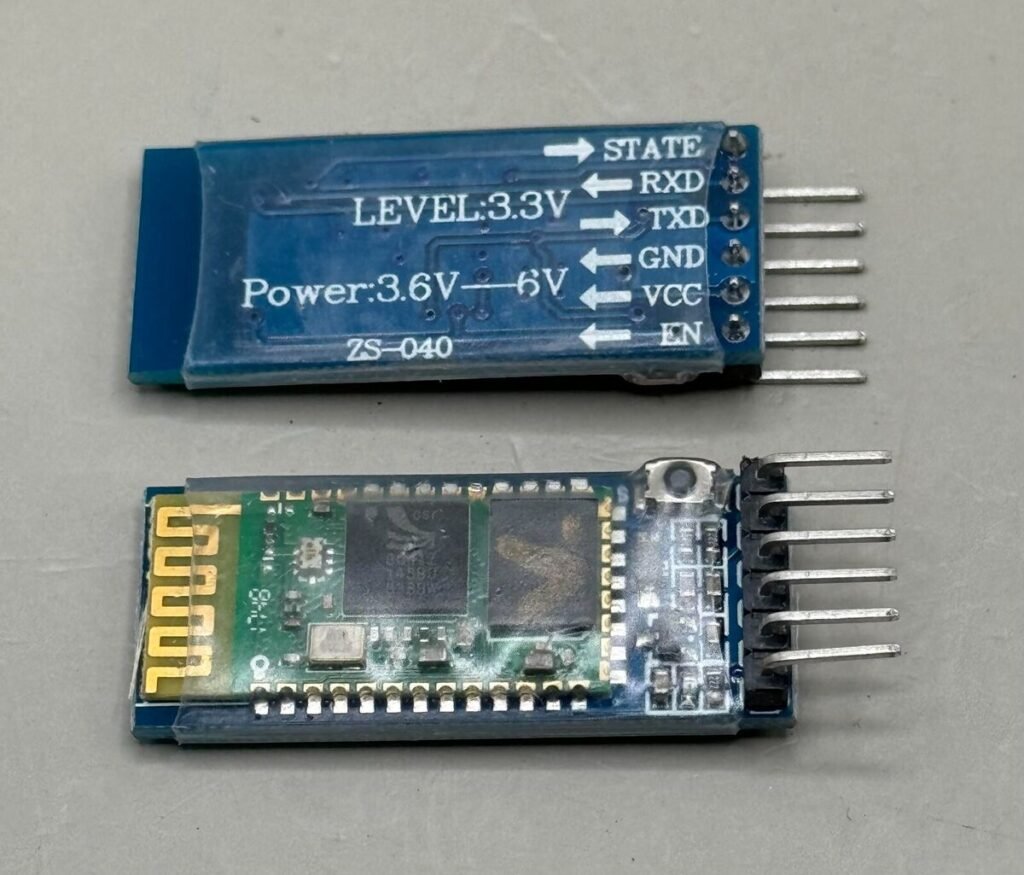
ZS-040 HC-05 Bluetooth Master/Slave Transceiver
Schematic
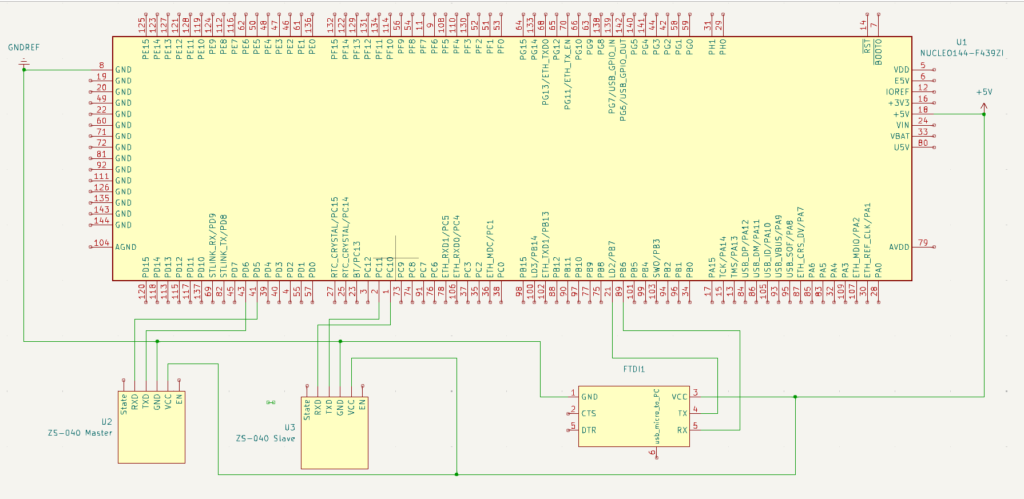
When setting up the Master Breadboard, only wire the U2/Master Bluetooth device. When setting up the Slave Breadboard, only wire the U3/Slave Bluetooth device. They need to be on difference breadboards to be able to communicate, because that’s how the code is written. If plugged and wired into the same breadboard with the same MCU, the Bluetooth devices will pair with each other but the code will not function correctly.
During Initialization, the MCU serial number will be used to indicate which board is the master and which is the slave. You’ll need to update the code to match your boards unique serial number. Line 444 in the example below uses the captured UUID/Serial # from the MCU to determine which is master or slave. We only need uid[0] which is the first part of the UUID, which is unique. The other bytes are production information, which is NOT unique. To get a better unique serial number using all 96 bits that is stored on the boards, visit my tutorial on: STM32XXX – Get UUID Unique Serial Number from Board
The USART2 & USART3 are configured from the MCU -> Bluetooth device where (MCU) TX-> (Bluetooth) Rx and (MCU) Rx-> (Bluetooth) Tx. The same methodology goes for USART1 which is Tx->Rx and Rx->Tx
char UUID[80] = {'\0'};
uint32_t uid[3] = {0x00};
uid[0] = HAL_GetUIDw0();
uid[1] = HAL_GetUIDw1();
uid[2] = HAL_GetUIDw2();
uint8_t lot1[4];
uint8_t lot2[4];
uint8_t *ptr;
ptr = (uint8_t *)&uid[1];
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
lot1[i] = ptr[i];
}
ptr = (uint8_t *)&uid[2];
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
lot2[i] = ptr[i];
}
sprintf(UUID, "0x%8.8lx:%c%c%c%c:%c%c%c%c", uid[0], lot1[0], lot1[1], lot1[2], lot1[3],
lot2[0], lot2[1], lot2[2], lot2[3]);
sprintf(serialNo, "0x%8.8lx", uid[0]);
printf("UUID: %s\r\n", UUID);
if (uid[0] == 0x0029002f) { // Change this value to be the ID that is returned by your MCU
printf("Master Init\r\n");
curRole = MASTER;
masterPhase = M_PHASE_0;
waitingOnResponse = false;
} else {
printf("Slave Init\r\n");
curRole = SLAVE;
slavePhase = S_PHASE_0;
waitingOnResponse = false;
waitingOnMaster = true;
}NOTE: The above example code will work for the most part, but there is a better way and in this example you can read more about it: How to get the unique ID of an STM32 Board using HAL_GetUIDwX
Pinouts & Configurations
Exploring the Source Code
main.h
/* USER CODE BEGIN Header */
/**
******************************************************************************
* @file : main.h
* @brief : Header for main.c file.
* This file contains the common defines of the application.
******************************************************************************
* @attention
*
* Copyright (c) 2024 STMicroelectronics.
* All rights reserved.
*
* This software is licensed under terms that can be found in the LICENSE file
* in the root directory of this software component.
* If no LICENSE file comes with this software, it is provided AS-IS.
*
******************************************************************************
*/
/* USER CODE END Header */
/* Define to prevent recursive inclusion -------------------------------------*/
#ifndef __MAIN_H
#define __MAIN_H
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
/* Includes ------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include "stm32f4xx_hal.h"
/* Private includes ----------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN Includes */
/* USER CODE END Includes */
/* Exported types ------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN ET */
/* USER CODE END ET */
/* Exported constants --------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN EC */
/* USER CODE END EC */
/* Exported macro ------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN EM */
/* USER CODE END EM */
/* Exported functions prototypes ---------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN EFP */
/* USER CODE END EFP */
/* Private defines -----------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN Private defines */
void _Error_Handler(const char *, int);
#define Error_Handler() _Error_Handler((const char *)__FILE__, __LINE__)
#define REDIRECT_PRINTF
/* USER CODE END Private defines */
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif /* __MAIN_H */
main.c
This code performs the redirection of output from printf to the USART1
/* Private user code ---------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN 0 */
#ifdef REDIRECT_PRINTF
#define PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE int __io_putchar(int ch)
#endif
#ifdef REDIRECT_PRINTF
/**
* @brief Retargets the C library printf function to the USART.
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE
{
/* Place your implementation of fputc here */
/* e.g. write a character to the USART1 */
HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart1, (uint8_t *)&ch, 1, 0xFFFF);
return ch;
}
#endifThis function processMaster() handles messages to and from the slave. It’s a state machine and as we progress through the message exchange, it changes the state we are in until we are done. Notice that we are delineating the end of each message with CR + LF (Carriage Return ) + (Line Feed). Without a CRLF at the end of each message the state machine would break;
void processMaster() {
HAL_StatusTypeDef halStatus = HAL_OK;
char obuf[1024];
int len = 0;
switch (masterPhase) {
case M_PHASE_0: {
if (!messageSent) {
sprintf(obuf, "Hello from Master\r\n");
printf("Master TxData: %s", obuf);
len = strlen(obuf);
halStatus = HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart2, (uint8_t *)&obuf[0], len, 0xFFFF);
if (halStatus != HAL_OK) {
Error_Handler();
}
messageSent = true;
recvdResponse = false;
} else {
if (messageSent && recvdResponse) {
printf("masterRxBuffer: %s\r\n", (char *) masterRxBuffer);
if (strcmp("OK", masterRxBuffer) == 0) {
recvdResponse = false;
waitingOnResponse = false;
messageSent = false;
waitingOnMaster = false;
masterPhase = M_SEND_SERIAL_NO_REQUEST;
}
}
}
break;
}
case M_SEND_SERIAL_NO_REQUEST: {
if (!messageSent) {
sprintf(obuf, "Serial#?\r\n");
printf("Master TxData: %s", obuf);
len = strlen(obuf);
halStatus = HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart2, (uint8_t *)&obuf[0], len, 0xFFFF);
if (halStatus != HAL_OK) {
Error_Handler();
}
messageSent = true;
recvdResponse = false;
} else {
if (messageSent && recvdResponse) {
printf("masterRxBuffer: %s\r\n", (char *) masterRxBuffer);
if (strncmp("Serial #:", masterRxBuffer, 9) == 0) {
sprintf(obuf, "Serial#: %s\r\n", masterRxBuffer + 9);
printf("Master RxData: %s", obuf);
recvdResponse = false;
waitingOnResponse = false;
messageSent = false;
waitingOnMaster = false;
masterPhase = M_PHASE_OK;
}
}
}
break;
}
case M_PHASE_OK: {
sprintf(obuf, "OK\r\n");
printf("Master RxData: %s", obuf);
recvdResponse = false;
waitingOnResponse = false;
messageSent = false;
waitingOnMaster = true;
masterPhase = M_DONE;
}
case M_DONE: {
break;
}
default: {
Error_Handler();
}
}
}This function processSlave() handles messages to and from the master. It’s a state machine and as we progress through the message exchange, it changes the state we are in until we are done. Notice that we are delineating the end of each message with CR + LF (Carriage Return ) + (Line Feed). Without a CRLF at the end of each message the state machine would break;
void processSlave() {
HAL_StatusTypeDef halStatus = HAL_OK;
char obuf[1024];
int len = 0;
switch (slavePhase) {
case S_PHASE_0: {
if (waitingOnMaster && recvdResponse) {
printf("slaveRxBuffer: %s\r\n", (char *) slaveRxBuffer);
if (strcmp("Hello from Master", slaveRxBuffer) == 0) {
recvdResponse = false;
waitingOnResponse = false;
messageSent = false;
waitingOnMaster = false;
slavePhase = S_PHASE_OK;
}
if (strcmp("Serial#?", slaveRxBuffer) == 0) {
recvdResponse = false;
waitingOnResponse = false;
messageSent = false;
waitingOnMaster = false;
slavePhase = S_PHASE_HANDLE_SERIAL_NO_REQUEST;
}
}
break;
}
case S_PHASE_HANDLE_SERIAL_NO_REQUEST: {
if (!waitingOnMaster) {
sprintf(obuf, "Serial #: %s\r\n", serialNo);
printf("Slave TxData: %s", obuf);
len = strlen(obuf);
halStatus = HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart3, (uint8_t *)&obuf[0], len, 0xFFFF);
if (halStatus != HAL_OK) {
Error_Handler();
}
recvdResponse = false;
waitingOnResponse = false;
messageSent = false;
waitingOnMaster = false;
slavePhase = S_PHASE_OK;
}
break;
}
case S_PHASE_OK: {
if (!waitingOnMaster) {
sprintf(obuf, "OK\r\n");
printf("Slave TxData: %s", obuf);
len = strlen(obuf);
halStatus = HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart3, (uint8_t *)&obuf[0], len, 0xFFFF);
if (halStatus != HAL_OK) {
Error_Handler();
}
recvdResponse = false;
waitingOnResponse = false;
messageSent = false;
waitingOnMaster = true;
slavePhase = S_PHASE_0;
}
break;
}
case S_DONE: {
break;
}
default: {
Error_Handler();
}
}
}These two functions are the initial message parsers. These are responsible for finding the ends of the messages by searching for a CR+LF. Once the CRLF is found, we find the CR and replace that character with a ‘\0’ character terminating the string. This buffer is sent up to the function (processMaster or processSlave) that runs the state machine to determine what to do with this message.
void recvMasterDeviceData() {
masterRxData[masterDeviceRx_indx ++] = masterRxByte; // Add data to Rx_Buffer
if (masterDeviceRx_indx >= 2) {
if (strncmp((char *) &masterRxData[masterDeviceRx_indx - 2], "\r\n", 2) == 0) {
strcpy(masterRxBuffer, (char *) masterRxData);
recvdResponse = true;
printf("Master RxData: %s", masterRxBuffer);
for (int i = strlen(masterRxBuffer); i >= 0; i --) {
if (masterRxBuffer[i] == '\r') {
masterRxBuffer[i] = '\0';
break;
}
}
memset(masterRxData, 0x00, sizeof(masterRxData));
masterDeviceRx_indx = 0;
}
}
}
void recvSlaveDeviceData() {
slaveRxData[slaveDeviceRx_indx ++] = slaveRxByte; // Add data to Rx_Buffer
if (slaveDeviceRx_indx >= 2) {
if (strncmp((char *) &slaveRxData[slaveDeviceRx_indx - 2], "\r\n", 4) == 0) {
strcpy(slaveRxBuffer, (char *) slaveRxData);
recvdResponse = true;
printf("Slave RxData: %s", slaveRxBuffer);
for (int i = strlen(slaveRxBuffer); i >= 0; i --) {
if (slaveRxBuffer[i] == '\r') {
slaveRxBuffer[i] = '\0';
break;
}
}
memset(slaveRxData, 0x00, sizeof(slaveRxData));
slaveDeviceRx_indx = 0;
}
}
}This function is a critical function for handling USART Receive Data (RxD). We chose to setup data receiving using an Interrupt methodology. By calling this HAL_UART_Receive_IT we setup the USART to call this function when a single byte is captured. When a byte of data is captured, we then determine which USART called this callback function and appropriately send it up to the handler: recvMasterDeviceData or recvSlaveDeviceData
void HAL_UART_RxCpltCallback(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart)
{
HAL_StatusTypeDef halStatus = HAL_OK;
if (huart->Instance == USART2) { // Blue Tooth Device
recvMasterDeviceData();
halStatus = HAL_UART_Receive_IT(&huart2, &masterRxByte, 1);
if (halStatus != HAL_OK) {
Error_Handler();
}
} else {
if (huart->Instance == USART3) { // Dumb terminal Device
recvSlaveDeviceData();
halStatus = HAL_UART_Receive_IT(&huart3, &slaveRxByte, 1);
if (halStatus != HAL_OK) {
Error_Handler();
}
}
}
}
/* USER CODE END 0 */This is the complete main function that kicks everything off.
/**
* @brief The application entry point.
* @retval int
*/
int main(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN 1 */
/* USER CODE END 1 */
/* MCU Configuration--------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Reset of all peripherals, Initializes the Flash interface and the Systick. */
HAL_Init();
/* USER CODE BEGIN Init */
/* USER CODE END Init */
/* Configure the system clock */
SystemClock_Config();
/* USER CODE BEGIN SysInit */
/* USER CODE END SysInit */
/* Initialize all configured peripherals */
MX_GPIO_Init();
MX_USART2_UART_Init();
MX_USART3_UART_Init();
MX_USART1_UART_Init();
/* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */
printf("\x1b[2J\x1b[H"); // Clear the dumb terminal screen
printf("Hello World!!!!\r\n");
HAL_UART_Receive_IT(&huart2, &masterRxByte, 1); // Initialize USART2 (Master Bluetooth) for Interrupt
HAL_UART_Receive_IT(&huart3, &slaveRxByte, 1); // Initialize USART3 (Slave Bluetooth) for Interrupt
char UUID[80] = {'\0'};
uint32_t uid[3] = {0x00};
uid[0] = HAL_GetUIDw0();
uid[1] = HAL_GetUIDw1();
uid[2] = HAL_GetUIDw2();
uint8_t lot1[4];
uint8_t lot2[4];
uint8_t *ptr;
ptr = (uint8_t *)&uid[1];
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
lot1[i] = ptr[i];
}
ptr = (uint8_t *)&uid[2];
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
lot2[i] = ptr[i];
}
sprintf(UUID, "0x%8.8lx:%c%c%c%c:%c%c%c%c", uid[0], lot1[0], lot1[1], lot1[2], lot1[3],
lot2[0], lot2[1], lot2[2], lot2[3]);
sprintf(serialNo, "0x%8.8lx", uid[0]);
printf("UUID: %s\r\n", UUID);
if (uid[0] == 0x0029002f) {
printf("Master Init\r\n");
curRole = MASTER;
masterPhase = M_PHASE_0;
waitingOnResponse = false;
} else {
printf("Slave Init\r\n");
curRole = SLAVE;
slavePhase = S_PHASE_0;
waitingOnResponse = false;
waitingOnMaster = true;
}
/* USER CODE END 2 */
/* Infinite loop */
/* USER CODE BEGIN WHILE */
bool done = false;
while (!done)
{
switch (curRole) {
case MASTER: {
processMaster();
break;
}
case SLAVE: {
processSlave();
break;
}
default: {
}
}
/* USER CODE END WHILE */
/* USER CODE BEGIN 3 */
}
/* USER CODE END 3 */
}The entire main.c source file
/* USER CODE BEGIN Header */
/**
******************************************************************************
* @file : main.c
* @brief : Main program body
******************************************************************************
* @attention
*
* Copyright (c) 2024 STMicroelectronics.
* All rights reserved.
*
* This software is licensed under terms that can be found in the LICENSE file
* in the root directory of this software component.
* If no LICENSE file comes with this software, it is provided AS-IS.
*
******************************************************************************
*/
/* USER CODE END Header */
/* Includes ------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include "main.h"
/* Private includes ----------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN Includes */
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdbool.h"
#include "string.h"
/* USER CODE END Includes */
/* Private typedef -----------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PTD */
typedef enum role {
UNKNOWN = 0,
SLAVE = 1,
MASTER = 2
} ROLE_t;
typedef enum masterPhases {
M_PHASE_0 = 0,
M_SEND_SERIAL_NO_REQUEST,
M_PHASE_OK,
M_DONE
} E_MPHASE_t;
typedef enum slavePhases {
S_PHASE_0 = 0,
S_PHASE_HANDLE_SERIAL_NO_REQUEST,
S_PHASE_OK,
S_DONE
} E_SPHASE_t;
/* USER CODE END PTD */
/* Private define ------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PD */
/* USER CODE END PD */
/* Private macro -------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PM */
/* USER CODE END PM */
/* Private variables ---------------------------------------------------------*/
UART_HandleTypeDef huart1;
UART_HandleTypeDef huart2;
UART_HandleTypeDef huart3;
/* USER CODE BEGIN PV */
bool messageSent = false;
bool recvdResponse = false;
bool waitingOnResponse = false;
bool waitingOnMaster = false;
E_MPHASE_t masterPhase;
E_SPHASE_t slavePhase;
uint8_t masterRxByte;
uint8_t slaveRxByte;
uint8_t masterDeviceRx_indx = 0;
uint8_t slaveDeviceRx_indx = 0;
uint8_t masterRxData[128];
uint8_t slaveRxData[128];
char masterRxBuffer[128];
char slaveRxBuffer[128];
char serialNo[80];
ROLE_t curRole = UNKNOWN;
/* USER CODE END PV */
/* Private function prototypes -----------------------------------------------*/
void SystemClock_Config(void);
static void MX_GPIO_Init(void);
static void MX_USART2_UART_Init(void);
static void MX_USART3_UART_Init(void);
static void MX_USART1_UART_Init(void);
/* USER CODE BEGIN PFP */
void processMaster(void);
void processSlave(void);
/* USER CODE END PFP */
/* Private user code ---------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN 0 */
#ifdef REDIRECT_PRINTF
#define PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE int __io_putchar(int ch)
#endif
#ifdef REDIRECT_PRINTF
/**
* @brief Retargets the C library printf function to the USART.
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE
{
/* Place your implementation of fputc here */
/* e.g. write a character to the USART2 and Loop until the end of transmission */
HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart1, (uint8_t *)&ch, 1, 0xFFFF);
return ch;
}
#endif
void processMaster() {
HAL_StatusTypeDef halStatus = HAL_OK;
char obuf[1024];
int len = 0;
switch (masterPhase) {
case M_PHASE_0: {
if (!messageSent) {
sprintf(obuf, "Hello from Master\r\n");
printf("Master TxData: %s", obuf);
len = strlen(obuf);
halStatus = HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart2, (uint8_t *)&obuf[0], len, 0xFFFF);
if (halStatus != HAL_OK) {
Error_Handler();
}
messageSent = true;
recvdResponse = false;
} else {
if (messageSent && recvdResponse) {
printf("masterRxBuffer: %s\r\n", (char *) masterRxBuffer);
if (strcmp("OK", masterRxBuffer) == 0) {
recvdResponse = false;
waitingOnResponse = false;
messageSent = false;
waitingOnMaster = false;
masterPhase = M_SEND_SERIAL_NO_REQUEST;
}
}
}
break;
}
case M_SEND_SERIAL_NO_REQUEST: {
if (!messageSent) {
sprintf(obuf, "Serial#?\r\n");
printf("Master TxData: %s", obuf);
len = strlen(obuf);
halStatus = HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart2, (uint8_t *)&obuf[0], len, 0xFFFF);
if (halStatus != HAL_OK) {
Error_Handler();
}
messageSent = true;
recvdResponse = false;
} else {
if (messageSent && recvdResponse) {
printf("masterRxBuffer: %s\r\n", (char *) masterRxBuffer);
if (strncmp("Serial #:", masterRxBuffer, 9) == 0) {
sprintf(obuf, "Serial#: %s\r\n", masterRxBuffer + 9);
printf("Master RxData: %s", obuf);
recvdResponse = false;
waitingOnResponse = false;
messageSent = false;
waitingOnMaster = false;
masterPhase = M_PHASE_OK;
}
}
}
break;
}
case M_PHASE_OK: {
sprintf(obuf, "OK\r\n");
printf("Master RxData: %s", obuf);
recvdResponse = false;
waitingOnResponse = false;
messageSent = false;
waitingOnMaster = true;
masterPhase = M_DONE;
}
case M_DONE: {
break;
}
default: {
Error_Handler();
}
}
}
void processSlave() {
HAL_StatusTypeDef halStatus = HAL_OK;
char obuf[1024];
int len = 0;
switch (slavePhase) {
case S_PHASE_0: {
if (waitingOnMaster && recvdResponse) {
printf("slaveRxBuffer: %s\r\n", (char *) slaveRxBuffer);
if (strcmp("Hello from Master", slaveRxBuffer) == 0) {
recvdResponse = false;
waitingOnResponse = false;
messageSent = false;
waitingOnMaster = false;
slavePhase = S_PHASE_OK;
}
if (strcmp("Serial#?", slaveRxBuffer) == 0) {
recvdResponse = false;
waitingOnResponse = false;
messageSent = false;
waitingOnMaster = false;
slavePhase = S_PHASE_HANDLE_SERIAL_NO_REQUEST;
}
}
break;
}
case S_PHASE_HANDLE_SERIAL_NO_REQUEST: {
if (!waitingOnMaster) {
sprintf(obuf, "Serial #: %s\r\n", serialNo);
printf("Slave TxData: %s", obuf);
len = strlen(obuf);
halStatus = HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart3, (uint8_t *)&obuf[0], len, 0xFFFF);
if (halStatus != HAL_OK) {
Error_Handler();
}
recvdResponse = false;
waitingOnResponse = false;
messageSent = false;
waitingOnMaster = false;
slavePhase = S_PHASE_OK;
}
break;
}
case S_PHASE_OK: {
if (!waitingOnMaster) {
sprintf(obuf, "OK\r\n");
printf("Slave TxData: %s", obuf);
len = strlen(obuf);
halStatus = HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart3, (uint8_t *)&obuf[0], len, 0xFFFF);
if (halStatus != HAL_OK) {
Error_Handler();
}
recvdResponse = false;
waitingOnResponse = false;
messageSent = false;
waitingOnMaster = true;
slavePhase = S_PHASE_0;
}
break;
}
case S_DONE: {
break;
}
default: {
Error_Handler();
}
}
}
void recvMasterDeviceData() {
masterRxData[masterDeviceRx_indx ++] = masterRxByte; // Add data to Rx_Buffer
if (masterDeviceRx_indx >= 2) {
if (strncmp((char *) &masterRxData[masterDeviceRx_indx - 2], "\r\n", 2) == 0) {
strcpy(masterRxBuffer, (char *) masterRxData);
recvdResponse = true;
printf("Master RxData: %s", masterRxBuffer);
for (int i = strlen(masterRxBuffer); i >= 0; i --) {
if (masterRxBuffer[i] == '\r') {
masterRxBuffer[i] = '\0';
break;
}
}
memset(masterRxData, 0x00, sizeof(masterRxData));
masterDeviceRx_indx = 0;
}
}
}
void recvSlaveDeviceData() {
slaveRxData[slaveDeviceRx_indx ++] = slaveRxByte; // Add data to Rx_Buffer
if (slaveDeviceRx_indx >= 2) {
if (strncmp((char *) &slaveRxData[slaveDeviceRx_indx - 2], "\r\n", 4) == 0) {
strcpy(slaveRxBuffer, (char *) slaveRxData);
recvdResponse = true;
printf("Slave RxData: %s", slaveRxBuffer);
for (int i = strlen(slaveRxBuffer); i >= 0; i --) {
if (slaveRxBuffer[i] == '\r') {
slaveRxBuffer[i] = '\0';
break;
}
}
memset(slaveRxData, 0x00, sizeof(slaveRxData));
slaveDeviceRx_indx = 0;
}
}
}
void HAL_UART_RxCpltCallback(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart)
{
HAL_StatusTypeDef halStatus = HAL_OK;
if (huart->Instance == USART2) { // Blue Tooth Device
recvMasterDeviceData();
halStatus = HAL_UART_Receive_IT(&huart2, &masterRxByte, 1);
if (halStatus != HAL_OK) {
Error_Handler();
}
} else {
if (huart->Instance == USART3) { // Dumb terminal Device
recvSlaveDeviceData();
halStatus = HAL_UART_Receive_IT(&huart3, &slaveRxByte, 1);
if (halStatus != HAL_OK) {
Error_Handler();
}
}
}
}
/* USER CODE END 0 */
/**
* @brief The application entry point.
* @retval int
*/
int main(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN 1 */
/* USER CODE END 1 */
/* MCU Configuration--------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Reset of all peripherals, Initializes the Flash interface and the Systick. */
HAL_Init();
/* USER CODE BEGIN Init */
/* USER CODE END Init */
/* Configure the system clock */
SystemClock_Config();
/* USER CODE BEGIN SysInit */
/* USER CODE END SysInit */
/* Initialize all configured peripherals */
MX_GPIO_Init();
MX_USART2_UART_Init();
MX_USART3_UART_Init();
MX_USART1_UART_Init();
/* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */
printf("\x1b[2J\x1b[H"); // Clear the dumb terminal screen
printf("Hello World!!!!\r\n");
HAL_UART_Receive_IT(&huart2, &masterRxByte, 1); // Initialize USART2 (Master Bluetooth) for Interrupt
HAL_UART_Receive_IT(&huart3, &slaveRxByte, 1); // Initialize USART3 (Slave Bluetooth) for Interrupt
char UUID[80] = {'\0'};
uint32_t uid[3] = {0x00};
uid[0] = HAL_GetUIDw0();
uid[1] = HAL_GetUIDw1();
uid[2] = HAL_GetUIDw2();
uint8_t lot1[4];
uint8_t lot2[4];
uint8_t *ptr;
ptr = (uint8_t *)&uid[1];
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
lot1[i] = ptr[i];
}
ptr = (uint8_t *)&uid[2];
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
lot2[i] = ptr[i];
}
sprintf(UUID, "0x%8.8lx:%c%c%c%c:%c%c%c%c", uid[0], lot1[0], lot1[1], lot1[2], lot1[3],
lot2[0], lot2[1], lot2[2], lot2[3]);
sprintf(serialNo, "0x%8.8lx", uid[0]);
printf("UUID: %s\r\n", UUID);
if (uid[0] == 0x0029002f) {
printf("Master Init\r\n");
curRole = MASTER;
masterPhase = M_PHASE_0;
waitingOnResponse = false;
} else {
printf("Slave Init\r\n");
curRole = SLAVE;
slavePhase = S_PHASE_0;
waitingOnResponse = false;
waitingOnMaster = true;
}
/* USER CODE END 2 */
/* Infinite loop */
/* USER CODE BEGIN WHILE */
bool done = false;
while (!done)
{
switch (curRole) {
case MASTER: {
processMaster();
break;
}
case SLAVE: {
processSlave();
break;
}
default: {
}
}
/* USER CODE END WHILE */
/* USER CODE BEGIN 3 */
}
/* USER CODE END 3 */
}
/**
* @brief System Clock Configuration
* @retval None
*/
void SystemClock_Config(void)
{
RCC_OscInitTypeDef RCC_OscInitStruct = {0};
RCC_ClkInitTypeDef RCC_ClkInitStruct = {0};
/** Configure the main internal regulator output voltage
*/
__HAL_RCC_PWR_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_PWR_VOLTAGESCALING_CONFIG(PWR_REGULATOR_VOLTAGE_SCALE1);
/** Initializes the RCC Oscillators according to the specified parameters
* in the RCC_OscInitTypeDef structure.
*/
RCC_OscInitStruct.OscillatorType = RCC_OSCILLATORTYPE_HSI;
RCC_OscInitStruct.HSIState = RCC_HSI_ON;
RCC_OscInitStruct.HSICalibrationValue = RCC_HSICALIBRATION_DEFAULT;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLState = RCC_PLL_ON;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLSource = RCC_PLLSOURCE_HSI;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLM = 8;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLN = 180;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLP = RCC_PLLP_DIV2;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLQ = 4;
if (HAL_RCC_OscConfig(&RCC_OscInitStruct) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/** Activate the Over-Drive mode
*/
if (HAL_PWREx_EnableOverDrive() != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/** Initializes the CPU, AHB and APB buses clocks
*/
RCC_ClkInitStruct.ClockType = RCC_CLOCKTYPE_HCLK|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_SYSCLK
|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_PCLK1|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_PCLK2;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.SYSCLKSource = RCC_SYSCLKSOURCE_PLLCLK;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.AHBCLKDivider = RCC_SYSCLK_DIV1;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.APB1CLKDivider = RCC_HCLK_DIV4;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.APB2CLKDivider = RCC_HCLK_DIV2;
if (HAL_RCC_ClockConfig(&RCC_ClkInitStruct, FLASH_LATENCY_5) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
}
/**
* @brief USART1 Initialization Function
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
static void MX_USART1_UART_Init(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN USART1_Init 0 */
/* USER CODE END USART1_Init 0 */
/* USER CODE BEGIN USART1_Init 1 */
/* USER CODE END USART1_Init 1 */
huart1.Instance = USART1;
huart1.Init.BaudRate = 19200;
huart1.Init.WordLength = UART_WORDLENGTH_8B;
huart1.Init.StopBits = UART_STOPBITS_1;
huart1.Init.Parity = UART_PARITY_NONE;
huart1.Init.Mode = UART_MODE_TX_RX;
huart1.Init.HwFlowCtl = UART_HWCONTROL_NONE;
huart1.Init.OverSampling = UART_OVERSAMPLING_16;
if (HAL_UART_Init(&huart1) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN USART1_Init 2 */
/* USER CODE END USART1_Init 2 */
}
/**
* @brief USART2 Initialization Function
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
static void MX_USART2_UART_Init(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN USART2_Init 0 */
/* USER CODE END USART2_Init 0 */
/* USER CODE BEGIN USART2_Init 1 */
/* USER CODE END USART2_Init 1 */
huart2.Instance = USART2;
huart2.Init.BaudRate = 38400;
huart2.Init.WordLength = UART_WORDLENGTH_8B;
huart2.Init.StopBits = UART_STOPBITS_1;
huart2.Init.Parity = UART_PARITY_NONE;
huart2.Init.Mode = UART_MODE_TX_RX;
huart2.Init.HwFlowCtl = UART_HWCONTROL_NONE;
huart2.Init.OverSampling = UART_OVERSAMPLING_16;
if (HAL_UART_Init(&huart2) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN USART2_Init 2 */
/* USER CODE END USART2_Init 2 */
}
/**
* @brief USART3 Initialization Function
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
static void MX_USART3_UART_Init(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN USART3_Init 0 */
/* USER CODE END USART3_Init 0 */
/* USER CODE BEGIN USART3_Init 1 */
/* USER CODE END USART3_Init 1 */
huart3.Instance = USART3;
huart3.Init.BaudRate = 38400;
huart3.Init.WordLength = UART_WORDLENGTH_8B;
huart3.Init.StopBits = UART_STOPBITS_1;
huart3.Init.Parity = UART_PARITY_NONE;
huart3.Init.Mode = UART_MODE_TX_RX;
huart3.Init.HwFlowCtl = UART_HWCONTROL_NONE;
huart3.Init.OverSampling = UART_OVERSAMPLING_16;
if (HAL_UART_Init(&huart3) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN USART3_Init 2 */
/* USER CODE END USART3_Init 2 */
}
/**
* @brief GPIO Initialization Function
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
static void MX_GPIO_Init(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN MX_GPIO_Init_1 */
/* USER CODE END MX_GPIO_Init_1 */
/* GPIO Ports Clock Enable */
__HAL_RCC_GPIOC_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_RCC_GPIOD_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_RCC_GPIOB_CLK_ENABLE();
/* USER CODE BEGIN MX_GPIO_Init_2 */
/* USER CODE END MX_GPIO_Init_2 */
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN 4 */
/**
* @brief This function is executed in case of error occurrence.
* @param file: The file name as string.
* @param line: The line in file as a number.
* @retval None
*/
void _Error_Handler(const char *file, int line)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN Error_Handler_Debug */
__disable_irq();
#ifdef REDIRECT_PRINTF
char buf[80];
sprintf(buf, "Trapped in Error_Handler(). Called from: %s, line: %d\r\n", file, line);
printf(buf);
#endif
/* User can add his own implementation to report the HAL error return state */
while(1)
{
}
}
/* USER CODE END 4 */
#ifdef USE_FULL_ASSERT
/**
* @brief Reports the name of the source file and the source line number
* where the assert_param error has occurred.
* @param file: pointer to the source file name
* @param line: assert_param error line source number
* @retval None
*/
void assert_failed(uint8_t *file, uint32_t line)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN 6 */
/* User can add his own implementation to report the file name and line number,
ex: printf("Wrong parameters value: file %s on line %d\r\n", file, line) */
/* USER CODE END 6 */
}
#endif /* USE_FULL_ASSERT */
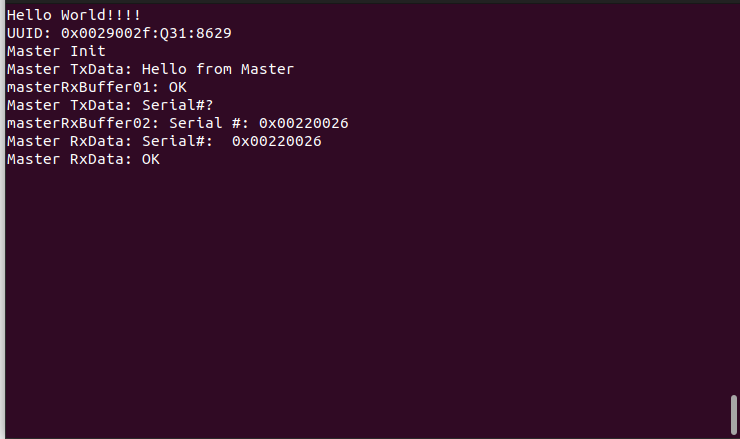
USART1 Dumb Terminal Output for Master Bluetooth
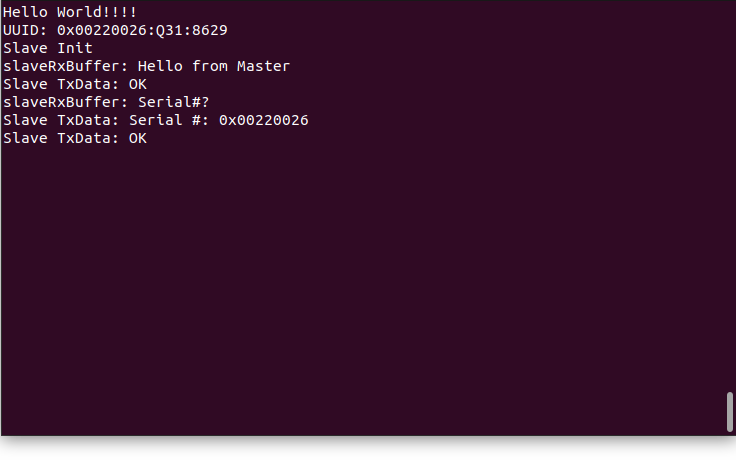
USART1 Dumb Terminal Output for Slave Bluetooth