Introduction
In this tutorial we will learn the fundamentals of setting and keeping time on your RTC using freeRTOS, LWIP and SNTP. We will use some of the key things we’ve learned in previous tutorials when setting up a network interface, and configuring DNS to find a hostname’s IP address.
In this project, we will be using the Nucleo-F439Zi board which includes an on board Real Time Clock, as well as an RJ-45 Ethernet connector to hookup to the local network. As long as the network we are connecting to has a route to the outside Internet, such as being able to connect to Google on a browser, this should work.
LWIP is the middle-ware that allows us to configure the Ethernet port and communicate with the outside world. SNTP is known as (Simple Network Time Protocol), allows us to talk to a NTP (Network Time Protocol) server on the Internet. The main purpose of these servers is to provide the client, (That’s Us), with the current UTC time by which we can set our internal clock to. These NTP servers provide highly accurate time down to the milliseconds. An overview of NTP can be found on this wiki.
Unix/Linux uses an epoch starting at 1/1/1970-00:00h (UTC) and NTP uses 1/1/1900-00:00h as its starting point. This leads to an offset equivalent to 70 years in seconds (there are 17 leap years between the two dates so the offset is to be substracted from NTP time to get Unix struct timeval.
(70*365 + 17)*86400 = 2208988800
We will use this formula to convert between the 2 different time EPOCH’s. We will #define NTP_TIMESTAMP_DIFF (2208988800) // 1900 to 1970 in seconds to use during the conversion process.
There is also a conversion that needs to be done on the sub-seconds as NTP time uses 64 bits and Unix/Linux uses 32 bits. The SNTP module under the LWIP middle-ware should handle this conversion.
FTDI Pinouts
FTDI to USB Pinout from right to left
- Pin 1 – GND
- Pin 2 – CTS
- Pin 3 – VCC
- Pin 4 – TX
- Pin 5 – RX
- Pin 6 – DTR
- USB Mini – Connect to PC via USB cable
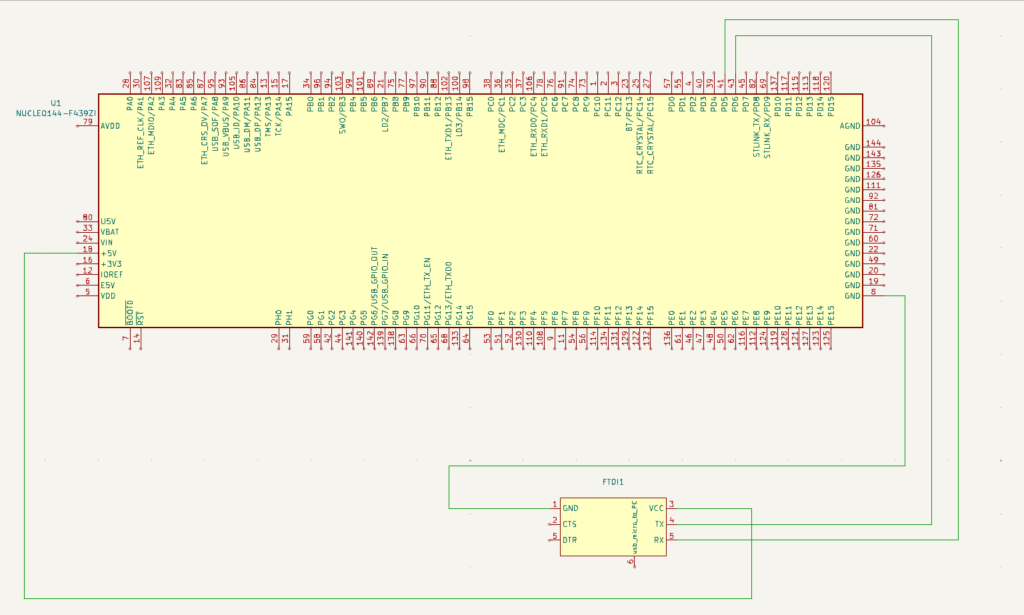
Make sure the jumper is set for 5v or 3v which ever is being used to power the FTDI device. If we look below at the schematic, it is showing in this case as 5v.

Nucleo-F439ZI
Schematic
Pinouts & Configurations
This is a generated PDF of all of the settings within the IOC file, which is included below. Parameters that have changed from the default values are highlighted by being in BOLD with an asterisk “*“
Exploring the Source Code
main.h
/* USER CODE BEGIN Header */
/**
******************************************************************************
* @file : main.h
* @brief : Header for main.c file.
* This file contains the common defines of the application.
******************************************************************************
* @attention
*
* Copyright (c) 2025 STMicroelectronics.
* All rights reserved.
*
* This software is licensed under terms that can be found in the LICENSE file
* in the root directory of this software component.
* If no LICENSE file comes with this software, it is provided AS-IS.
*
******************************************************************************
*/
/* USER CODE END Header */
/* Define to prevent recursive inclusion -------------------------------------*/
#ifndef __MAIN_H
#define __MAIN_H
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
/* Includes ------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include "stm32f4xx_hal.h"
/* Private includes ----------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN Includes */
/* USER CODE END Includes */
/* Exported types ------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN ET */
/* USER CODE END ET */
/* Exported constants --------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN EC */
/* USER CODE END EC */
/* Exported macro ------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN EM */
/* USER CODE END EM */
/* Exported functions prototypes ---------------------------------------------*/
void Error_Handler(void);
/* USER CODE BEGIN EFP */
/* USER CODE END EFP */
/* Private defines -----------------------------------------------------------*/
#define MCO_Pin GPIO_PIN_0
#define MCO_GPIO_Port GPIOH
#define RMII_MDC_Pin GPIO_PIN_1
#define RMII_MDC_GPIO_Port GPIOC
#define RMII_REF_CLK_Pin GPIO_PIN_1
#define RMII_REF_CLK_GPIO_Port GPIOA
#define RMII_MDIO_Pin GPIO_PIN_2
#define RMII_MDIO_GPIO_Port GPIOA
#define RMII_CRS_DV_Pin GPIO_PIN_7
#define RMII_CRS_DV_GPIO_Port GPIOA
#define RMII_RXD0_Pin GPIO_PIN_4
#define RMII_RXD0_GPIO_Port GPIOC
#define RMII_RXD1_Pin GPIO_PIN_5
#define RMII_RXD1_GPIO_Port GPIOC
#define RMII_TXD1_Pin GPIO_PIN_13
#define RMII_TXD1_GPIO_Port GPIOB
#define TCK_Pin GPIO_PIN_14
#define TCK_GPIO_Port GPIOA
#define RMII_TX_EN_Pin GPIO_PIN_11
#define RMII_TX_EN_GPIO_Port GPIOG
#define RMII_TXD0_Pin GPIO_PIN_13
#define RMII_TXD0_GPIO_Port GPIOG
/* USER CODE BEGIN Private defines */
#define REDIRECT_PRINTF
/* USER CODE END Private defines */
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif /* __MAIN_H */
main.c
/* USER CODE BEGIN Header */
/**
******************************************************************************
* @file : main.c
* @brief : Main program body
******************************************************************************
* @attention
*
* Copyright (c) 2025 STMicroelectronics.
* All rights reserved.
*
* This software is licensed under terms that can be found in the LICENSE file
* in the root directory of this software component.
* If no LICENSE file comes with this software, it is provided AS-IS.
*
******************************************************************************
*/
/* USER CODE END Header */
/* Includes ------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include "main.h"
#include "cmsis_os.h"
#include "lwip.h"
/* Private includes ----------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN Includes */
#include "semphr.h"
#include "stdbool.h"
#include "dnsLookup.h"
#include "mysntp.h"
/* USER CODE END Includes */
/* Private typedef -----------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PTD */
/* USER CODE END PTD */
/* Private define ------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PD */
/* USER CODE END PD */
/* Private macro -------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PM */
/* USER CODE END PM */
/* Private variables ---------------------------------------------------------*/
RTC_HandleTypeDef hrtc;
UART_HandleTypeDef huart2;
/* Definitions for networkTask */
osThreadId_t networkTaskHandle;
const osThreadAttr_t networkTask_attributes = {
.name = "networkTask",
.stack_size = 256 * 4,
.priority = (osPriority_t) osPriorityNormal,
};
/* Definitions for sntpTask */
osThreadId_t sntpTaskHandle;
const osThreadAttr_t sntpTask_attributes = {
.name = "sntpTask",
.stack_size = 512 * 4,
.priority = (osPriority_t) osPriorityLow,
};
/* Definitions for displayTimeTask */
osThreadId_t displayTimeTaskHandle;
const osThreadAttr_t displayTimeTask_attributes = {
.name = "displayTimeTask",
.stack_size = 512 * 4,
.priority = (osPriority_t) osPriorityLow,
};
/* USER CODE BEGIN PV */
bool waitingOnNetwork = true;
bool dhcpReady = false;
bool waitingOnSNTP = true;
SemaphoreHandle_t rtcSemaphore;
/* USER CODE END PV */
/* Private function prototypes -----------------------------------------------*/
void SystemClock_Config(void);
static void MX_GPIO_Init(void);
static void MX_USART2_UART_Init(void);
static void MX_RTC_Init(void);
void networkInitializationTask(void *argument);
void sntpInitializationTask(void *argument);
void displayTimeWorker(void *argument);
/* USER CODE BEGIN PFP */
void link_myCallBack(struct netif *netif);
/* USER CODE END PFP */
/* Private user code ---------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN 0 */
#ifdef REDIRECT_PRINTF
#define PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE int __io_putchar(int ch)
#endif
#ifdef REDIRECT_PRINTF
PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE
{
HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart2, (uint8_t *)&ch, 1, 0xFFFF);
return ch;
}
#endif
#define ETH_DEVICE 0
void link_myCallBack(struct netif *netif) {
uint32_t regValue = 0;
if (HAL_ETH_ReadPHYRegister(&heth, ETH_DEVICE, PHY_BSR, ®Value) == HAL_OK) {
if((regValue & PHY_LINKED_STATUS) == (uint16_t)RESET) {
if (!netif_is_link_up(netif)) { // Link status = disconnected
netif_set_down(netif);
printf("Network cable is now disconnected!!!\r\n");
netif_set_link_down(netif);
}
} else {
if (netif_is_link_up(netif)) { // Link status = connected
printf("Network cable is now connected!!!\r\n");
printf("Rebooting the system!!!\r\n");
osDelay(2000);
// We could try to write some sort of recovery logic to handle a reconnection, however.... (Boom!!!)
NVIC_SystemReset(); // Reboot the microprocessor and start the application over.
}
}
}
}
void displayRTCInfo() {
struct tm timePtr;
float secfrac;
getRtcDateTime(&timePtr, &secfrac);
char timeBuf[30];
RTC_TimeTypeDef sTime;
sTime.Hours = timePtr.tm_hour;
sTime.Minutes = timePtr.tm_min;
sTime.Seconds = timePtr.tm_sec;
sTime.DayLightSaving = RTC_DAYLIGHTSAVING_NONE;
sTime.StoreOperation = RTC_STOREOPERATION_RESET;
char microSeconds[16];
sprintf(microSeconds, "%3.3f", secfrac / 1000.0);
char *usPtr = NULL;
usPtr = microSeconds + 1; // Drop the decimal point in the string to print seconds with microseconds as xx.ususus
sprintf(timeBuf, "\x1b[HRTC Time: %02d:%02d:%02d%s\r\n", sTime.Hours, sTime.Minutes, sTime.Seconds, usPtr);
// sprintf(timeBuf, "\x1b[HRTC Time: %02d:%02d:%02d", sTime.Hours, sTime.Minutes, sTime.Seconds);
printf(timeBuf);
fflush(stdout);
}
/* USER CODE END 0 */
/**
* @brief The application entry point.
* @retval int
*/
int main(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN 1 */
/* USER CODE END 1 */
/* MCU Configuration--------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Reset of all peripherals, Initializes the Flash interface and the Systick. */
HAL_Init();
/* USER CODE BEGIN Init */
/* USER CODE END Init */
/* Configure the system clock */
SystemClock_Config();
/* USER CODE BEGIN SysInit */
/* USER CODE END SysInit */
/* Initialize all configured peripherals */
MX_GPIO_Init();
MX_USART2_UART_Init();
MX_RTC_Init();
/* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */
/* USER CODE END 2 */
/* Init scheduler */
osKernelInitialize();
/* USER CODE BEGIN RTOS_MUTEX */
/* add mutexes, ... */
/* USER CODE END RTOS_MUTEX */
/* USER CODE BEGIN RTOS_SEMAPHORES */
/* add semaphores, ... */
rtcSemaphore = xSemaphoreCreateMutex();
/* USER CODE END RTOS_SEMAPHORES */
/* USER CODE BEGIN RTOS_TIMERS */
/* start timers, add new ones, ... */
/* USER CODE END RTOS_TIMERS */
/* USER CODE BEGIN RTOS_QUEUES */
/* add queues, ... */
/* USER CODE END RTOS_QUEUES */
/* Create the thread(s) */
/* creation of networkTask */
networkTaskHandle = osThreadNew(networkInitializationTask, NULL, &networkTask_attributes);
/* creation of sntpTask */
sntpTaskHandle = osThreadNew(sntpInitializationTask, NULL, &sntpTask_attributes);
/* creation of displayTimeTask */
displayTimeTaskHandle = osThreadNew(displayTimeWorker, NULL, &displayTimeTask_attributes);
/* USER CODE BEGIN RTOS_THREADS */
/* add threads, ... */
/* USER CODE END RTOS_THREADS */
/* USER CODE BEGIN RTOS_EVENTS */
/* add events, ... */
/* USER CODE END RTOS_EVENTS */
/* Start scheduler */
osKernelStart();
/* We should never get here as control is now taken by the scheduler */
/* Infinite loop */
/* USER CODE BEGIN WHILE */
while (1)
{
/* USER CODE END WHILE */
/* USER CODE BEGIN 3 */
}
/* USER CODE END 3 */
}
/**
* @brief System Clock Configuration
* @retval None
*/
void SystemClock_Config(void)
{
RCC_OscInitTypeDef RCC_OscInitStruct = {0};
RCC_ClkInitTypeDef RCC_ClkInitStruct = {0};
/** Configure the main internal regulator output voltage
*/
__HAL_RCC_PWR_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_PWR_VOLTAGESCALING_CONFIG(PWR_REGULATOR_VOLTAGE_SCALE1);
/** Initializes the RCC Oscillators according to the specified parameters
* in the RCC_OscInitTypeDef structure.
*/
RCC_OscInitStruct.OscillatorType = RCC_OSCILLATORTYPE_HSI|RCC_OSCILLATORTYPE_HSE;
RCC_OscInitStruct.HSEState = RCC_HSE_ON;
RCC_OscInitStruct.HSIState = RCC_HSI_ON;
RCC_OscInitStruct.HSICalibrationValue = RCC_HSICALIBRATION_DEFAULT;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLState = RCC_PLL_ON;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLSource = RCC_PLLSOURCE_HSI;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLM = 8;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLN = 180;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLP = RCC_PLLP_DIV2;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLQ = 4;
if (HAL_RCC_OscConfig(&RCC_OscInitStruct) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/** Activate the Over-Drive mode
*/
if (HAL_PWREx_EnableOverDrive() != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/** Initializes the CPU, AHB and APB buses clocks
*/
RCC_ClkInitStruct.ClockType = RCC_CLOCKTYPE_HCLK|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_SYSCLK
|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_PCLK1|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_PCLK2;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.SYSCLKSource = RCC_SYSCLKSOURCE_PLLCLK;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.AHBCLKDivider = RCC_SYSCLK_DIV1;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.APB1CLKDivider = RCC_HCLK_DIV4;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.APB2CLKDivider = RCC_HCLK_DIV2;
if (HAL_RCC_ClockConfig(&RCC_ClkInitStruct, FLASH_LATENCY_5) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
}
/**
* @brief RTC Initialization Function
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
static void MX_RTC_Init(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN RTC_Init 0 */
/* USER CODE END RTC_Init 0 */
RTC_TimeTypeDef sTime = {0};
RTC_DateTypeDef sDate = {0};
/* USER CODE BEGIN RTC_Init 1 */
/* USER CODE END RTC_Init 1 */
/** Initialize RTC Only
*/
hrtc.Instance = RTC;
hrtc.Init.HourFormat = RTC_HOURFORMAT_24;
hrtc.Init.AsynchPrediv = 125-1;
hrtc.Init.SynchPrediv = 8000-1;
hrtc.Init.OutPut = RTC_OUTPUT_DISABLE;
hrtc.Init.OutPutPolarity = RTC_OUTPUT_POLARITY_HIGH;
hrtc.Init.OutPutType = RTC_OUTPUT_TYPE_OPENDRAIN;
if (HAL_RTC_Init(&hrtc) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN Check_RTC_BKUP */
/* USER CODE END Check_RTC_BKUP */
/** Initialize RTC and set the Time and Date
*/
sTime.Hours = 0;
sTime.Minutes = 0;
sTime.Seconds = 0;
sTime.DayLightSaving = RTC_DAYLIGHTSAVING_NONE;
sTime.StoreOperation = RTC_STOREOPERATION_RESET;
if (HAL_RTC_SetTime(&hrtc, &sTime, RTC_FORMAT_BIN) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
sDate.WeekDay = RTC_WEEKDAY_MONDAY;
sDate.Month = RTC_MONTH_JANUARY;
sDate.Date = 1;
sDate.Year = 0;
if (HAL_RTC_SetDate(&hrtc, &sDate, RTC_FORMAT_BIN) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN RTC_Init 2 */
/* USER CODE END RTC_Init 2 */
}
/**
* @brief USART2 Initialization Function
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
static void MX_USART2_UART_Init(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN USART2_Init 0 */
/* USER CODE END USART2_Init 0 */
/* USER CODE BEGIN USART2_Init 1 */
/* USER CODE END USART2_Init 1 */
huart2.Instance = USART2;
huart2.Init.BaudRate = 19200;
huart2.Init.WordLength = UART_WORDLENGTH_8B;
huart2.Init.StopBits = UART_STOPBITS_1;
huart2.Init.Parity = UART_PARITY_NONE;
huart2.Init.Mode = UART_MODE_TX_RX;
huart2.Init.HwFlowCtl = UART_HWCONTROL_NONE;
huart2.Init.OverSampling = UART_OVERSAMPLING_16;
if (HAL_UART_Init(&huart2) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN USART2_Init 2 */
/* USER CODE END USART2_Init 2 */
}
/**
* @brief GPIO Initialization Function
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
static void MX_GPIO_Init(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN MX_GPIO_Init_1 */
/* USER CODE END MX_GPIO_Init_1 */
/* GPIO Ports Clock Enable */
__HAL_RCC_GPIOC_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_RCC_GPIOH_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_RCC_GPIOA_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_RCC_GPIOB_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_RCC_GPIOD_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_RCC_GPIOG_CLK_ENABLE();
/* USER CODE BEGIN MX_GPIO_Init_2 */
/* USER CODE END MX_GPIO_Init_2 */
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN 4 */
/* USER CODE END 4 */
/* USER CODE BEGIN Header_networkInitializationTask */
/**
* @brief Function implementing the networkTask thread.
* @param argument: Not used
* @retval None
*/
/* USER CODE END Header_networkInitializationTask */
void networkInitializationTask(void *argument)
{
/* init code for LWIP */
MX_LWIP_Init();
/* USER CODE BEGIN 5 */
extern struct netif gnetif;
osDelay(2000);
char *ipstr = NULL;
while (ip4_addr_isany_val(*netif_ip4_addr(&gnetif))) {
osDelay(200);
}
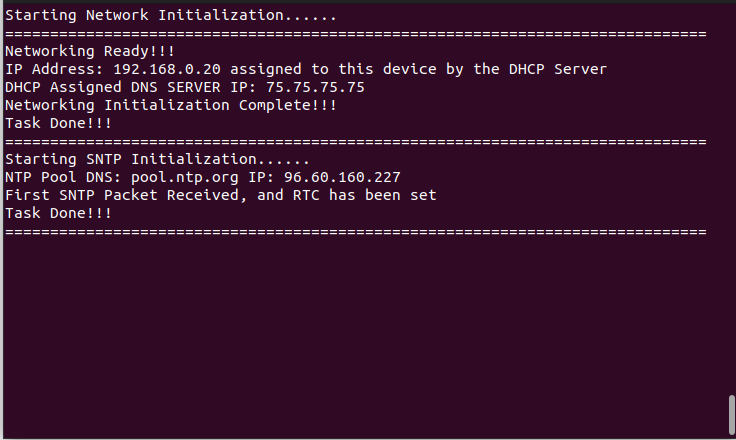
printf("\x1b[2J\x1b[H"); // Clear the dumb terminal screen
printf("Starting Network Initialization......\r\n");
char buffer[128];
printf("==============================================================================\n\r");
ipstr = ip4addr_ntoa(netif_ip4_addr(&gnetif));
sprintf(buffer, "Networking Ready!!!\r\n");
printf(buffer);
sprintf(buffer, "IP Address: %s assigned to this device by the DHCP Server\r\n", ipstr);
printf(buffer);
const ip_addr_t *ipaddr;
ipaddr = dns_getserver(0);
dhcpReady = !(ip4_addr_isany_val(*ipaddr));
while (!dhcpReady) {
osDelay(200);
ipaddr = dns_getserver(0);
dhcpReady = !(ip4_addr_isany_val(*ipaddr));
}
sprintf(buffer, "DHCP Assigned DNS SERVER IP: %s\r\n", ip4addr_ntoa(ipaddr));
printf(buffer);
// Here we override the default callback defined in the MX_LWIP_Init() function which defaults to:
// netif_set_link_callback(&gnetif, ethernet_link_status_updated);
//
// Setup our callback to handle ethernet cable disconnect/reconnect and override the default callback of: ethernet_link_status_updated
netif_set_link_callback(&gnetif, link_myCallBack);
sprintf(buffer, "Networking Initialization Complete!!!\r\n");
printf(buffer);
printf("Task Done!!!\r\n");
printf("==============================================================================\n\r");
waitingOnNetwork = false;
/* Infinite loop */
for(;;)
{
osDelay(1);
}
/* USER CODE END 5 */
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN Header_sntpInitializationTask */
/**
* @brief Function implementing the sntpTask thread.
* @param argument: Not used
* @retval None
*/
/* USER CODE END Header_sntpInitializationTask */
void sntpInitializationTask(void *argument)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN sntpInitializationTask */
char buffer[64];
dnsGetHostName_t getHostNameResp;
while (waitingOnNetwork) {
osDelay(10);
}
printf("Starting SNTP Initialization......\r\n");
getHostNameResp.name = "pool.ntp.org";
getHostNameResp.done = false;
bool found = getHostByName(getHostNameResp.name, &getHostNameResp);
while (!found || getHostNameResp.done == false) {
osDelay(10);
}
sprintf(buffer, "NTP Pool DNS: %s IP: %s\r\n", getHostNameResp.name, ip4addr_ntoa(&getHostNameResp.addr));
printf(buffer);
initSntp(&getHostNameResp.addr);
waitingOnSNTP = false;
printf("First SNTP Packet Received, and RTC has been set\n\r");
printf("Task Done!!!\r\n");
printf("==============================================================================\n\r");
/* Infinite loop */
for(;;)
{
osDelay(1);
}
/* USER CODE END sntpInitializationTask */
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN Header_displayTimeWorker */
/**
* @brief Function implementing the displayTimeTask thread.
* @param argument: Not used
* @retval None
*/
/* USER CODE END Header_displayTimeWorker */
void displayTimeWorker(void *argument)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN displayTimeWorker */
while (waitingOnNetwork || waitingOnSNTP) {
osDelay(1);
}
osDelay(2000);
printf("\x1b[2J\x1b[H"); // Clear the dumb terminal screen
printf("\x1b[H"); // Cursor Home
/* Infinite loop */
for(;;)
{
displayRTCInfo();
osDelay(100);
}
/* USER CODE END displayTimeWorker */
}
/**
* @brief Period elapsed callback in non blocking mode
* @note This function is called when TIM6 interrupt took place, inside
* HAL_TIM_IRQHandler(). It makes a direct call to HAL_IncTick() to increment
* a global variable "uwTick" used as application time base.
* @param htim : TIM handle
* @retval None
*/
void HAL_TIM_PeriodElapsedCallback(TIM_HandleTypeDef *htim)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN Callback 0 */
/* USER CODE END Callback 0 */
if (htim->Instance == TIM6) {
HAL_IncTick();
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN Callback 1 */
/* USER CODE END Callback 1 */
}
/**
* @brief This function is executed in case of error occurrence.
* @retval None
*/
void Error_Handler(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN Error_Handler_Debug */
/* User can add his own implementation to report the HAL error return state */
__disable_irq();
while (1)
{
}
/* USER CODE END Error_Handler_Debug */
}
#ifdef USE_FULL_ASSERT
/**
* @brief Reports the name of the source file and the source line number
* where the assert_param error has occurred.
* @param file: pointer to the source file name
* @param line: assert_param error line source number
* @retval None
*/
void assert_failed(uint8_t *file, uint32_t line)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN 6 */
/* User can add his own implementation to report the file name and line number,
ex: printf("Wrong parameters value: file %s on line %d\r\n", file, line) */
printf("Wrong parameters value: file %s on line %ld\r\n", file, line);
while(1) {
}
/* USER CODE END 6 */
}
#endif /* USE_FULL_ASSERT */
dnslookup.h
/*
* dnsLookup.h
*
* Created on: Jun 7, 2024
* Author: johng
*/
#ifndef DNSLOOKUP_H_
#define DNSLOOKUP_H_
#include "cmsis_os.h"
#include "stm32f4xx_hal.h"
#include "lwip/dns.h"
#include "err.h"
#include "lwip.h"
#include "stdbool.h"
#include "lwip/apps/sntp.h"
typedef struct dnsGetHostName {
const char *name;
ip_addr_t addr;
bool done;
} dnsGetHostName_t;
//extern dnsGetHostName_t *getHostNameResp;
void hostNameFoundCallBack(const char *, const ip_addr_t *, void *);
bool getHostByName(const char *, dnsGetHostName_t *);
typedef void (*callBackFuncPtr)(char *, ip_addr_t *, void *);
typedef void (*dns_found_callback)(const char *name, const ip_addr_t *ipaddr, void *callback_arg);
#endif /* DNSLOOKUP_H_ */
dnslookup.c
The hostNameFoundCallBack function will be called when the DNS server that was sent a request to resolve a hostname, has returned an answer to our query. If the query to get the hostname, was successful,
we will get an IP address returned to us. Requesting information from a server is generally handled as an asynchronous event. We request data from a server, and at some point in time, the server will respond.
Therefore, it is common to have callback routines or event handler code to intercept the response and deal with it. This is very common when communicating with remote servers because of the time delay in the
responses.
#include "dnsLookup.h"
dnsGetHostName_t *getHostNameRespPtr;
void hostNameFoundCallBack(const char *hostname, const ip_addr_t *ipaddr, void *arg)
{
char buffer[128];
if (ipaddr != NULL) {
/* Address resolved, send request */
getHostNameRespPtr->addr = *ipaddr;
getHostNameRespPtr->done = true;
} else {
sprintf(buffer, "DNS Failed to resolve. ipaddr == NULL\r\n");
printf(buffer);
Error_Handler();
}
}
bool getHostByName(const char *name, dnsGetHostName_t *response) {
bool retVal = false;
int counter = 0;
char buffer[128];
getHostNameRespPtr = response;
/*
* The following function call is used to get the a host name via a DNS server. The DNS server had to be previously setup during
* static setup or through DHCP initialization.
* Once a response from the DNS Server is received, the callback function specified in the 3rd parameter is invoked.
* In this case the callback function is called: hostNameFoundCallBack
*/
err_enum_t err = dns_gethostbyname(name, &getHostNameRespPtr->addr, (dns_found_callback) hostNameFoundCallBack, NULL);
if (err == ERR_INPROGRESS) {
while(getHostNameRespPtr->done != true) {
osDelay(100);
counter ++;
if (counter > 1000) {
sprintf(buffer, "getHosNameRespPtr never returned TRUE after X Number of tries.\r\n");
printf(buffer);
Error_Handler();
}
}
retVal = true;
} else if (err == ERR_OK) {
getHostNameRespPtr->done = true;
retVal = true;
} else {
sprintf(buffer, "dns_gethostbyname ERROR: %d", err);
printf(buffer);
Error_Handler();
}
return retVal;
}
mysntp.h
/*
* sntp.h
*
* Created on: Jun 8, 2024
* Author: johng
*/
#ifndef MYSNTP_H_
#define MYSNTP_H_
#include "cmsis_os.h"
#include "stm32f4xx_hal.h"
#include "lwip/apps/sntp.h"
#include "RTC.h"
#include "stdbool.h"
//define USE_FULL_LL_DRIVER
//include "stm32f4xx_ll_rtc.h"
#define SNTP_SET_SYSTEM_TIME_NTP(sec, us) sntp_set_system_time_us(sec, us)
#define NTP_TIMESTAMP_DIFF (2208988800) // 1900 to 1970 in seconds
void sntp_set_system_time_us(u32_t sec, u32_t us);
void sntp_get_system_time_us(s32_t *sec, u32_t *us);
void initSntp(ip_addr_t *);
#endif /* MYSNTP_H_ */
mysntp.c
As with requesting DNS information, we also have the same delayed response issue with SNTP requests. We have defined a callback function such that when the SNTP response has successfully returned
a NTP time, we can handle that response appropriately.
Note that on line 42, we are initializing the sntp_setoperatingmode to SNTP_OPMODE_POLL. We also setup the polling using SNTP_UPDATE_DELAY to be 30000ms (Milliseconds) or every 30 seconds.
Every time this timer expires, the callback function sntp_set_system_time_us is invoked.
/*
* sntp.c
*
* Created on: Jun 8, 2024
* Author: johng
*/
#include "mysntp.h"
#include "stdbool.h"
#include "time.h"
bool sntpFlagDone = false;
bool recvdSNTP_Resp = false;
struct timeval tv = {0};
static struct tm *sntp_tm;
void sntp_set_system_time_us(u32_t sec, u32_t us) {
time_t ut;
/*
Unix uses an epoch located at 1/1/1970-00:00h (UTC) and NTP uses 1/1/1900-00:00h.
This leads to an offset equivalent to 70 years in seconds (there are 17 leap years between the two dates so the offset is
(70*365 + 17)*86400 = 2208988800
to be substracted from NTP time to get Unix struct timeval.
*/
ut = ( time_t ) ( sec - NTP_TIMESTAMP_DIFF );
tv.tv_sec = ut;
tv.tv_usec = us;
sntp_tm = gmtime(&ut);
sntp_tm->tm_isdst = 1;
setRtcDateTime(sntp_tm);
sntpFlagDone = true;
}
void initSntp(ip_addr_t *ipaddr) {
sntp_setoperatingmode(SNTP_OPMODE_POLL);
sntp_setserver(0, ipaddr);
sntp_init();
while (!sntpFlagDone) {
osDelay(1);
}
}
RTC.h
/*
* RTC.h
*
* Created on: Mar 4, 2025
* Author: johng
*/
#ifndef RTC_H_
#define RTC_H_
#include "main.h"
#include "cmsis_os.h"
#include "stm32f4xx_hal.h"
#include "time.h"
#include "semphr.h"
void setRtcDateTime (struct tm *timePtr);
HAL_StatusTypeDef getRtcDateTime(struct tm *timePtr, float *secfrac);
#endif /* RTC_H_ */
RTC.c
In this code, it was necessary to utilize semaphores. This is because we cannot allow two tasks to interact with the RTC at the same time. When one task has been started to set or read to/from the RTC, we must allow that task to complete. Therefore, we have to allow code to set the date/time complete before allowing
a get of the date/time to occur. Semaphores are like traffic cops, that allow traffic to flow or not flow based on conditions or timing. In this case if we are attempting to read the date/time, at the same time as another task is setting the date/time, the read operation will have to wait. The same is true when attempting to read the date/time, such that a set date/time operation will have to wait until the read is done.
Notice on lines 43, and 51 we are setting both the Time and the Date. We are doing this because it is REQUIRED to set both to complete the updating of the RTC. You should also, read the time and date as well, as shown on lines 87 and 88.
You can read more about Semaphores in this article: FreeRTOS binary semaphores
/*
* RTC.c
*
* Created on: Mar 5, 2025
* Author: johng
*/
#include "RTC.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "string.h"
extern RTC_HandleTypeDef hrtc;
extern SemaphoreHandle_t rtcSemaphore;
void setRtcDateTime (struct tm *timePtr)
{
int status = 0;
HAL_StatusTypeDef halStatus = HAL_OK;
RTC_TimeTypeDef sTime = {0};
RTC_DateTypeDef sDate = {0};
if(rtcSemaphore != NULL) {
/* See if we can obtain the semaphore. If the semaphore is not
available wait 10 ticks to see if it becomes free. */
status = xSemaphoreTake(rtcSemaphore, (TickType_t) 10);
if(status == pdTRUE) {
/* We were able to obtain the semaphore and can now access the
shared resource. */
/** Initialize RTC and set the Time and Date
*/
sTime.Hours = timePtr->tm_hour;
sTime.Minutes = timePtr->tm_min;
sTime.Seconds = timePtr->tm_sec;
sTime.DayLightSaving = RTC_DAYLIGHTSAVING_NONE;
sTime.StoreOperation = RTC_STOREOPERATION_RESET;
sDate.WeekDay = timePtr->tm_wday + 1;
sDate.Month = timePtr->tm_mon + 1;
sDate.Date = timePtr->tm_mday;
sDate.Year = timePtr->tm_year - 100;
if ((halStatus = HAL_RTC_SetTime(&hrtc, &sTime, RTC_FORMAT_BIN)) != HAL_OK)
{
char buf[80];
sprintf(buf, "HAL_RTC_SetTime returned %d\r\n", halStatus);
printf(buf);
Error_Handler();
}
if ((halStatus = HAL_RTC_SetDate(&hrtc, &sDate, RTC_FORMAT_BIN)) != HAL_OK)
{
char buf[80];
sprintf(buf, "HAL_RTC_SetDate returned %d\r\n", halStatus);
printf(buf);
Error_Handler();
}
xSemaphoreGive(rtcSemaphore);
} else {
/* We could not obtain the semaphore and can therefore not access
the shared resource safely. */
printf("Could not acquire a semaphore for rtcSemaphore.\r\n");
Error_Handler();
}
} else {
printf("rtcSemaphore is NULL.\r\n");
Error_Handler();
}
}
HAL_StatusTypeDef getRtcDateTime(struct tm *timePtr, float *secfrac) {
HAL_StatusTypeDef halStatus = HAL_OK;
RTC_TimeTypeDef sTime;
RTC_DateTypeDef sDate;
int status = 0;
if(rtcSemaphore != NULL) {
/* See if we can obtain the semaphore. If the semaphore is not
available wait 10 ticks to see if it becomes free. */
status = xSemaphoreTake(rtcSemaphore, (TickType_t) 10);
if(status == pdTRUE) {
/* We were able to obtain the semaphore and can now access the
shared resource. */
HAL_RTC_GetTime(&hrtc, &sTime, RTC_FORMAT_BIN);
HAL_RTC_GetDate(&hrtc, &sDate, RTC_FORMAT_BIN);
timePtr->tm_hour = sTime.Hours;
timePtr->tm_min = sTime.Minutes;
timePtr->tm_sec = sTime.Seconds;
timePtr->tm_isdst = sTime.DayLightSaving;
timePtr->tm_wday = sDate.WeekDay - 1;
timePtr->tm_mon = sDate.Month - 1;
timePtr->tm_mday = sDate.Date;
timePtr->tm_year = sDate.Year + 100;
float frac;
frac = ((float)((sTime.SecondFraction - sTime.SubSeconds) * 1000.0)) / ((float)(sTime.SecondFraction + 1));
*secfrac = frac;
xSemaphoreGive(rtcSemaphore);
} else {
/* We could not obtain the semaphore and can therefore not access
the shared resource safely. */
printf("Could not acquire a semaphore for rtcSemaphore.\r\n");
Error_Handler();
}
} else {
printf("rtcSemaphore is NULL.\r\n");
Error_Handler();
}
return(halStatus);
}
ethernetif.c
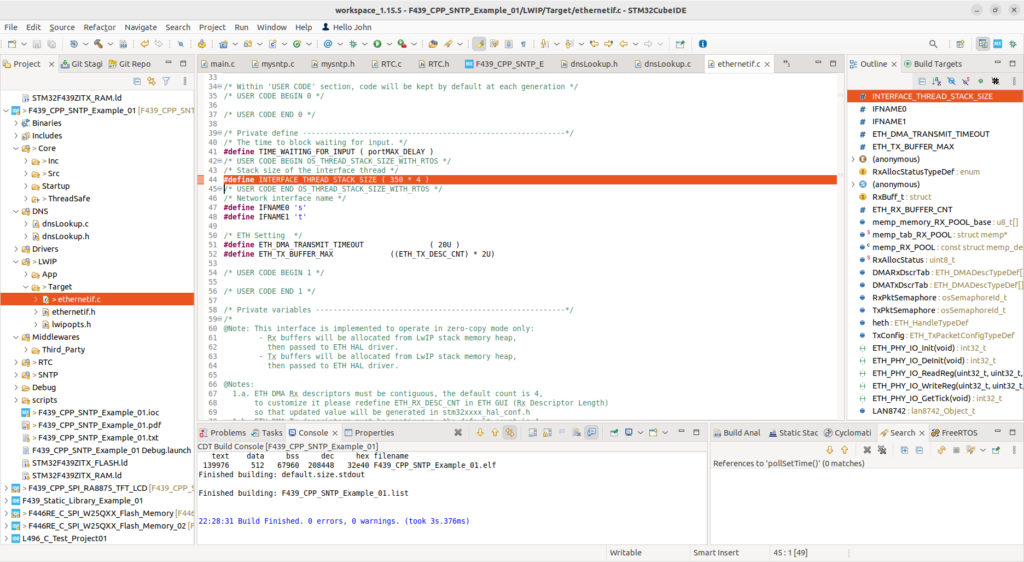
We have to modify the ethernetif.c file because the default value for INTERFACE_THREAD_STACK_SIZE is only 350, which is too small. I’ve increased this 4 times, as shown on line: 44 below.
USART Output